Colchicine is an anti-inflammatory medication commonly used to treat gout. It works by reducing inflammation and pain during acute gout attacks. This drug is not a long-term solution but is effective at providing relief during flare-ups. Colchicine may be prescribed as an oral tablet or capsule.
Colchicine works by inhibiting the migration of white blood cells to the inflamed area, reducing the inflammatory response and alleviating pain. It is most effective when taken at the first sign of a gout attack.
Side effects of colchicine can include diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal discomfort. It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for dosing, as excessive use can lead to toxicity.
Dosage Form – Specialty Drug
Tablets: Colchicine 1 mg.
Drug Class – Action
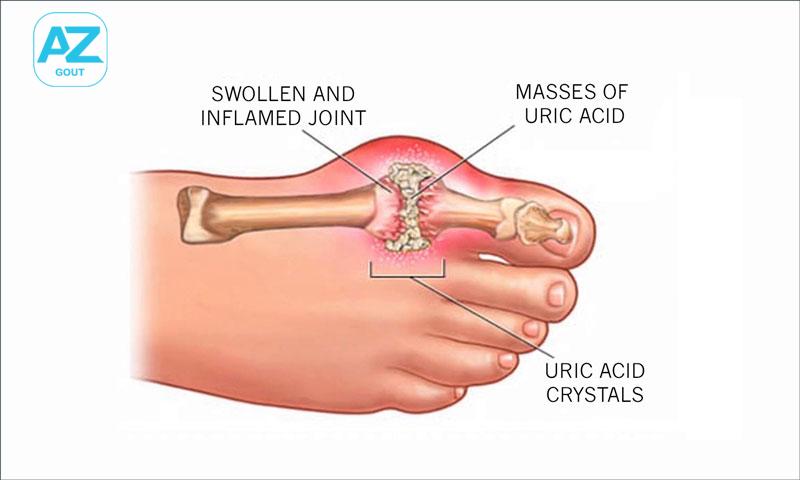
Treatment of gout.
Indications
Prevention and treatment of acute gout attacks. Acute gout due to urate crystal deposits. Periodic fever, Behcet’s disease.
Contraindications
Severe kidney or liver impairment, risk of narrow-angle glaucoma, urinary obstruction, pregnant women.
Adverse Effects
Common: Gastrointestinal disturbances, headache, rash. Rare: Muscle pain, decreased white blood cells, reduced sperm with recovery.
Dosage and Administration
- Acute Gout:
- Monotherapy: Initiate with 1 mg, then take an additional 0.5 mg after 1 hour, continue with 0.5 mg once or twice daily (up to 3 times daily) for 5 – 7 days.
- Combination therapy: 1 mg per day, in combination with NSAID or corticosteroid.
- Prevention of acute gout attacks while taking uric acid-lowering medications: Take 0.5 mg once or up to 3 times daily.
Caution
Allow at least 3 days between each course of acute gout treatment. Diarrhea is an early sign of colchicine overdose. Discontinue the medication or reduce the dose when diarrhea occurs.
Pregnant women: Category D (TGA) (*), Category C (FDA) (**).
Breastfeeding women: Avoid use.
Dose adjustment is necessary for patients with renal impairment.
(*) Category D as per TGA classification: Drugs which have caused or may be suspected of causing harm to the fetus or permanent damage to the fetus without the possibility of recovery.
(**) Category C as per FDA classification: Animal studies have shown adverse effects on the fetus (teratogenicity, embryolethality, other) and there are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Use of the drug in pregnant women should only be considered when the potential benefits outweigh the possible risks to the fetus.