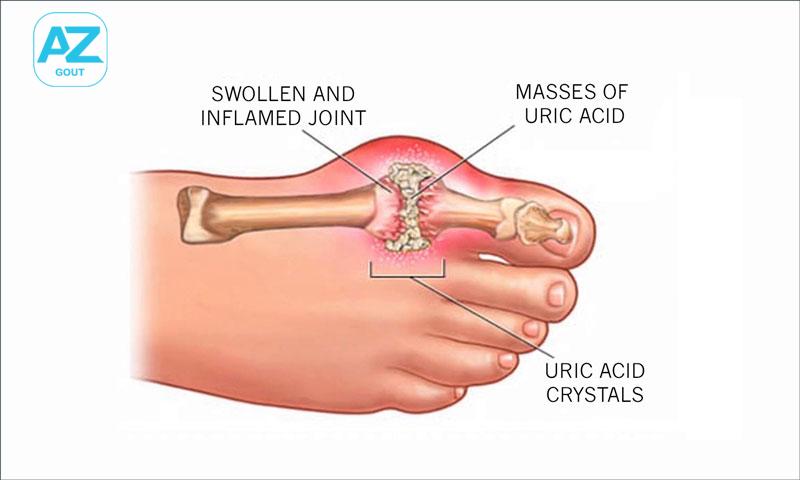
Gout is one of the characteristic joint-related diseases associated with the body’s metabolism of uric acid. Currently, the prevalence of this disease is gradually increasing and trending towards affecting younger individuals. So, what are the signs of gout that help detect it early for effective treatment?
Overview of Gout and its Severity
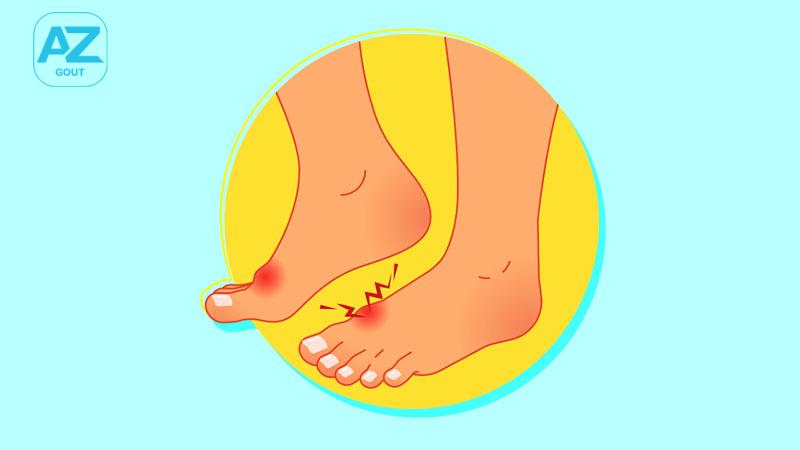
Gout, also known as “goutte” in French, and “thống phong” in Chinese, is a form of joint inflammation that causes redness and swelling, leading to severe, sudden pain in specific joints, especially the big toe, ankle, wrist, and hand.
This condition is related to the metabolic process of uric acid in the body and has a high likelihood of recurrence, especially under favorable conditions. Therefore, early recognition of gout symptoms is crucial for comprehensive treatment.
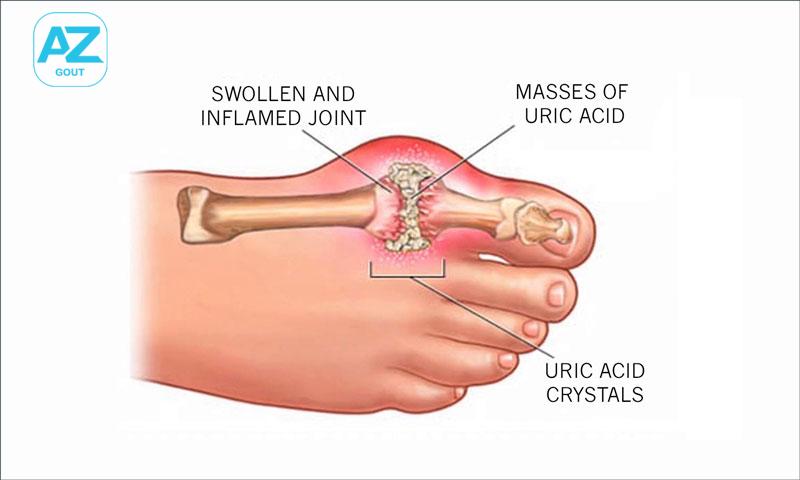
Some studies indicate that the prevalence of gout is higher in males than females, especially among individuals aged 30 to 60. Due to current lifestyle trends, unhealthy dietary habits, and inadequate physical activity, the incidence of gout is rising, and there is a tendency for it to affect younger individuals.
Gout can cause significant inconvenience to patients, potentially impacting their daily lives. However, gout can be treated and recurrence can be limited if symptoms are detected early, treated correctly, and healthy living habits are established.
Causes of Gout
Gout is caused by a disorder in the body’s metabolism of uric acid. In healthy individuals, uric acid results from the breakdown of purines within DNA and RNA. It can also be produced from the degradation of nucleic acid from ingested food or dead cells. Once formed, uric acid moves into the blood and is filtered by the kidneys to be excreted.
If the concentration of uric acid in the blood increases or is not properly excreted, it can accumulate as urate crystals in various tissues, particularly in joint spaces. This accumulation leads to inflammation, joint pain, and is diagnosed as gout.
Gout can be caused by genetic factors or external environmental influences. Some factors contributing to elevated blood acid levels include:
- Reduced excretion of uric acid.
- Kidney diseases leading to gout due to uric acid accumulation.
- Cardiovascular diseases such as high blood pressure and acute inflammation.
- Excessive consumption of animal protein-rich foods, especially seafood, organ meats, and egg yolks.
- Excessive alcohol consumption and stimulant use, increasing the risk of gout.
- Use of medications that elevate uric acid levels, such as chemotherapy drugs, diuretics, and drugs for treating hypertension.
- Family history of gout
Signs of Gout
Recognizing the following signs of gout can help facilitate early detection and effective treatment:
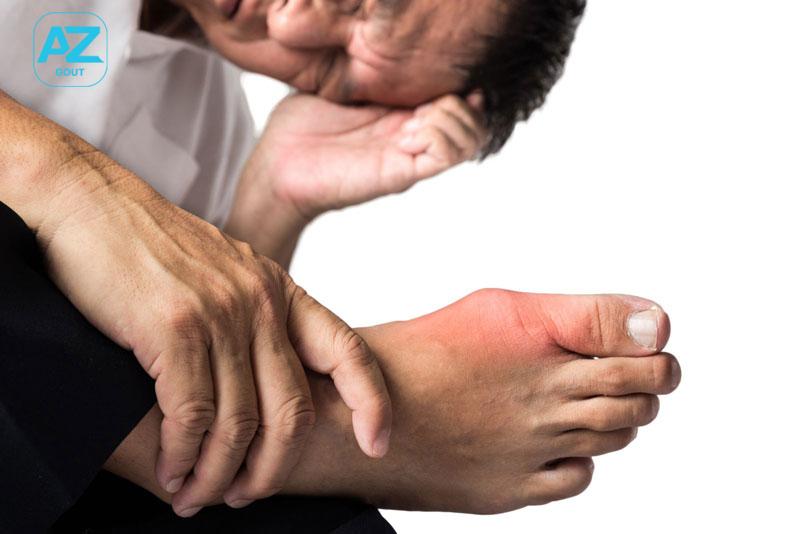
- Intense pain in joints, especially at night.
- Inflamed joints with redness, warmth, and tenderness upon touch.
- Gout attacks typically last around 5-7 days and gradually subside. Normal joint function returns after the pain subsides.
- Limited mobility due to joint pain during attacks.
Observing unusual bodily signs should prompt individuals to seek prompt medical attention and undergo relevant tests for accurate diagnosis. Essential diagnostic tests may include blood tests, X-rays, ultrasound, and joint fluid analysis.
Complications of Gout
Patients who do not seek early medical attention are at risk of facing dangerous complications caused by gout. Complications associated with gout include:
- Frequent disease recurrence: Even after successful treatment, gout can recur, causing persistent pain. If the condition is not controlled early, it may lead to joint destruction.
- Formation of tophi within joints: Untreated gout can result in the formation of tophi, visible as lumps on cartilage around joints such as the ears, elbows, and toes. This can cause joint stiffness and swelling, leading to deformities and reduced joint mobility.
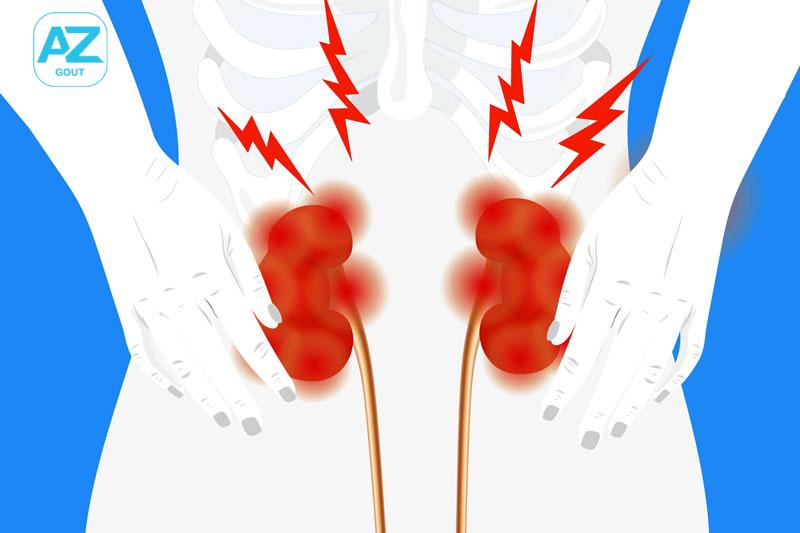
- Kidney stones: Excessive urate crystal accumulation can damage the kidneys, leading to stone formation within the urinary system
Preventing Gout
Incorporating the following habits into daily life can help slow the progression of gout:
- Follow medical instructions and prescriptions strictly; do not self-administer or discontinue prescribed medications without consulting a doctor.
- Adhere to scheduled check-ups to monitor the disease’s progression and address any unusual issues promptly.
- Comprehensive treatment of underlying diseases contributing to gout, such as metabolic disorders.
- Engage in regular physical exercise.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
Particularly, gout patients should pay attention to maintaining a balanced diet:
- Avoid animal organ meats, especially liver and kidney.
- Minimize consumption of purine-rich foods and proteins, especially from seafood and red meat.
- Limit saturated fat intake and choose low-fat products.
- Include fiber-rich foods in the diet, such as cucumber, turnip, and tomatoes.
- Use natural sugars found in vegetables, fruits, and whole grains instead of refined sugars.
- Drink plenty of water daily, around 2.5 to 3 liters.
- Limit alcohol consumption, especially beer and spirits.
- Avoid coffee, tea, and carbonated drinks.

Recognizing the symptoms of gout as described above can help individuals identify the condition early and seek timely treatment. Paying attention to one’s health and preventing illness is the best approach.