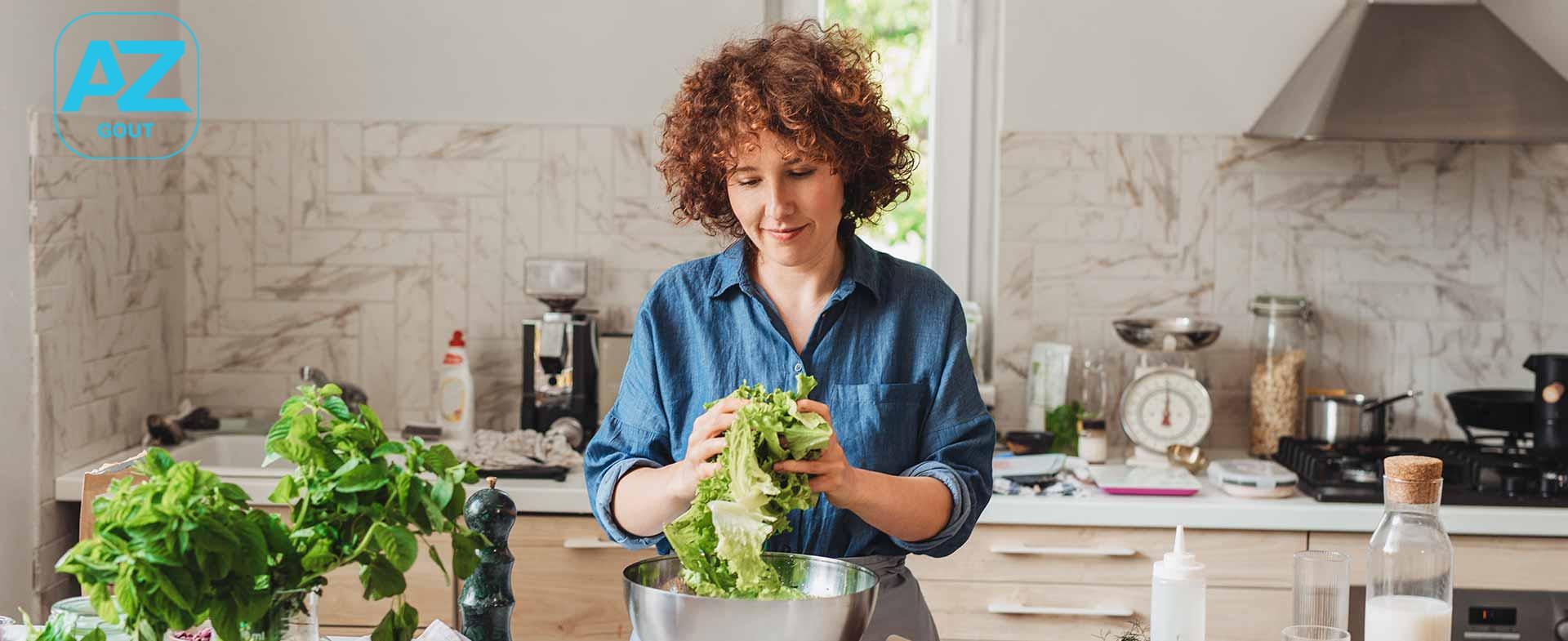
When you’re trying to lose weight, the idea of eating more might sound counterintuitive. However, volume eating, which focuses on “high-volume” foods, can help you feel full while consuming fewer calories. Instead of cutting out certain foods or entire food groups, volume eating allows you to eat satisfying portions that help you stay on track with your weight loss goals.
1. What is Volume Eating?
1.1. The Concept Behind Volume Eating
Volume eating is based on the principle that feeling full is influenced more by the quantity of food rather than the calorie count. According to Sarah Hutchinson, RDN, a registered dietitian at Henry Ford Health, “Feeling full depends on the amount of food you eat, not the number of calories and fat grams.” This approach allows you to consume larger portions of food without exceeding your calorie limits, making it easier to manage hunger and maintain a calorie deficit.
1.2. High-Volume vs. Low-Volume Foods
The key to volume eating is understanding the energy density of foods. Foods high in energy density, such as processed snacks, sodas, and desserts, pack a lot of calories into small portions. On the other hand, low-energy-density foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provide more volume for fewer calories.
2. Focus on Filling Foods
2.1. Prioritizing Low-Energy-Dense Foods
To successfully practice volume eating, prioritize foods that are high in water and fiber content, as these tend to be low in energy density. For example, you can eat a large portion of vegetables like broccoli, kale, and celery, which are low in calories but high in volume, keeping you full for longer.
2.2. The Benefits of High-Volume Foods
“High-volume, low-energy dense foods typically take longer for your body to digest,” says Hutchinson. This means they can help you stay satisfied between meals. For example, snacking on a whole apple is more filling than eating a small portion of potato chips, even if both snacks contain roughly the same number of calories.
For more on how to incorporate these foods into your diet, visit Health.gov’s Dietary Guidelines.
3. How to Determine the Volume of a Food
3.1. Understanding Energy Density
Energy density is the measure of calories relative to the weight or volume of food. Foods with a high water content, like fruits and vegetables, generally have a low energy density. This means you can eat more of them without consuming too many calories.
3.2. Practical Tips for Volume Eating
To maximize the benefits of volume eating:
- Incorporate a variety of vegetables into meals to add bulk without extra calories.
- Choose whole fruits over fruit juices or dried fruits, which are higher in sugar and calories.
- Opt for whole grains like brown rice and oats, which provide more volume and fiber than their refined counterparts.
For more insights on managing portion sizes and energy density, check out the CDC’s Guide to Healthy Eating.
4. Conclusion: Volume Eating for Weight Loss
Volume eating offers a sustainable approach to weight loss by allowing you to enjoy satisfying portions without overloading on calories. By focusing on high-volume, low-energy dense foods, you can keep hunger at bay and stay on track with your weight loss goals.